
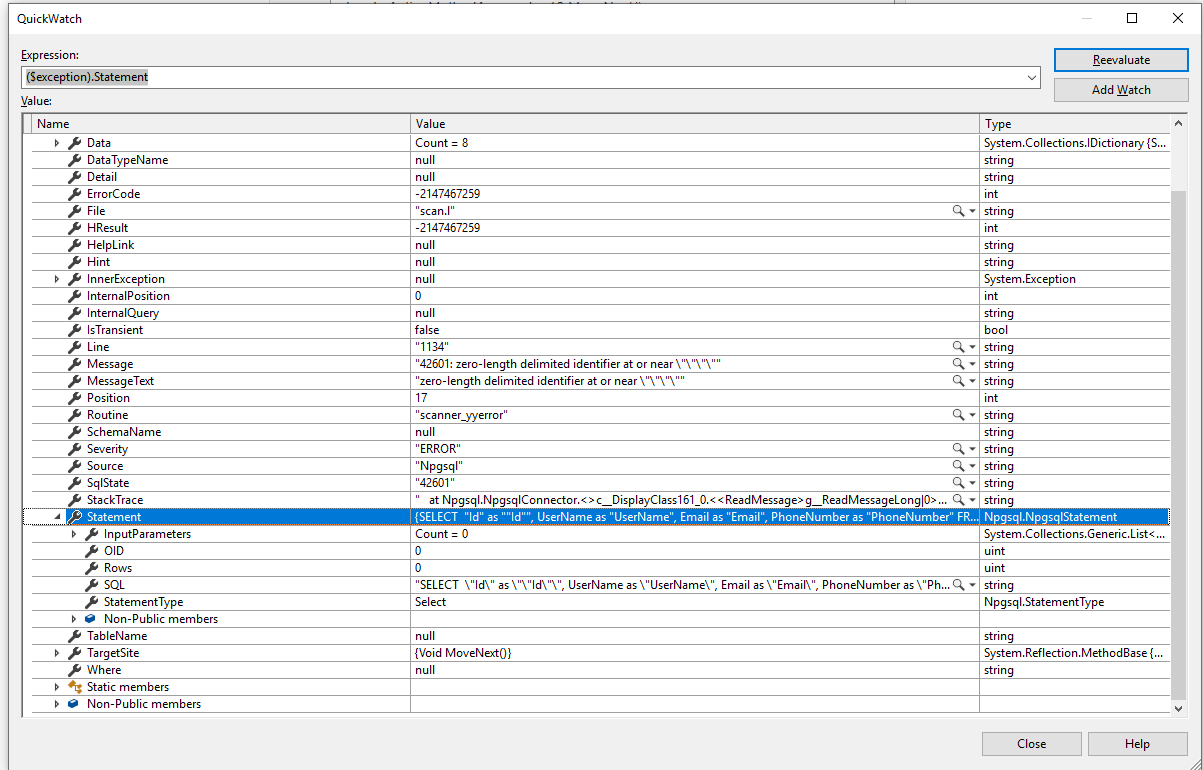
In this example, let's only dump users over the age of 40. To do this, we wrap our query in parentheses and pass it as the first argument to the copy command. The copy command also supports queries on table being dumped. Now if we cat our CSV again, we should see that we only have the name and email from our users table. In this case, let's just select name and email from our users. If we only want specific columns from our table, we can pass them as a comma separated list after our table name. This time when we cat our output file, we can see that the headers have been added to the top. To include headers in the generated csv file, you can pass "with csv header" to the copy command after specifying the output file path. You'll notice that our CSV file doesn't have headers. Once the copy command has finished running, we can cat the newly generated file. Let's dump this data into a CSV using the copy command. If we select from the table we can see that we have a few rows of data. We can see from inspecting the users table that we have a few columns. In this example, we're using a dummy database with a table called users. The copy command expects a table as an argument, followed by the absolute path for the outputted csv file. This gives the shopkeeper the desired result so that he can begin his audit:Ĭopying data with INSERT INTO can also be done with conditions.We can generate a CSV from table data in Postgres using the copy command. In order to copy data from all the tables, the shopkeeper can use UNION to merge the tables together in the subquery: This query uses a subquery to find all values in “hardware” and then adds them to the “masterlist”. For example to copy all items from the table “hardware” to the table “masterlist” the following query can be run: When using INSERT INTO with the VALUES command it is possible to add entries by hand, however a query can also be used in place of the VALUES command. It is often used to insert single values into tables by running the command as such: This command inserts specified values into a specified table. This can be done using the INSERT command. Now that the shopkeeper’s master list has been created and structured, the data needs to be inserted into the table. With this done, the shopkeeper now has the following tables:

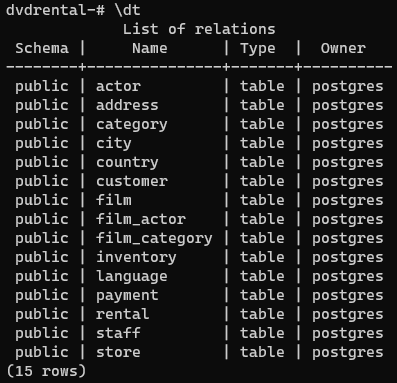
The shopkeeper can use this to create his master list: Once filled out, this command will create a new table with the same table structure, but without any data. The easiest way to create a table with the same table structure as a different table is to use:ĬREATE TABLE AS TABLE WITH NO DATA The master list needs to have the same table structure (columns, data-types, etc.). The shopkeeper needs to first make a new table to contain the data. In order to create a master list that contains all of the store’s items and prices the shopkeeper needs to create the table for all items and copy the data from each of the departments into the new table. However the data he needs exist in separate tables containing the inventories of each department: Take for example a shopkeeper who needs to create a master list of all the items in his store to conduct a store-wide audit.
#Postgres copy table update#
It can be used to update an inventory, create a table that has different permissions than the original, and much more.
INSERT INTO SELECT FROM WHERE Ĭopying data between tables is just as easy as querying data however it will take a bit longer to run than a normal query.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
